Data Breach Explained: Types, Use Cases, and Prevention Tips
Consider how much personal information you keep online — bank information, photos, work files, or even health records. Now, picture that a stranger has stolen or leaked that data. That’s what is known as a Data Breach, and it’s one of the greatest risks in these digital times.
Companies lose billions of dollars every year, while individuals have their trust violated, their privacy invaded — and sometimes they’re robbed. If you want to stay safe — or even reach the next level in a cybersecurity career — you must learn what data breaches are, why they happen, and how to stop them.
What is a Data Breach?
A data breach occurs when information that is sensitive or protected is accessed without authorization. That stolen data can be passwords, credit card information, health records, or company secrets.
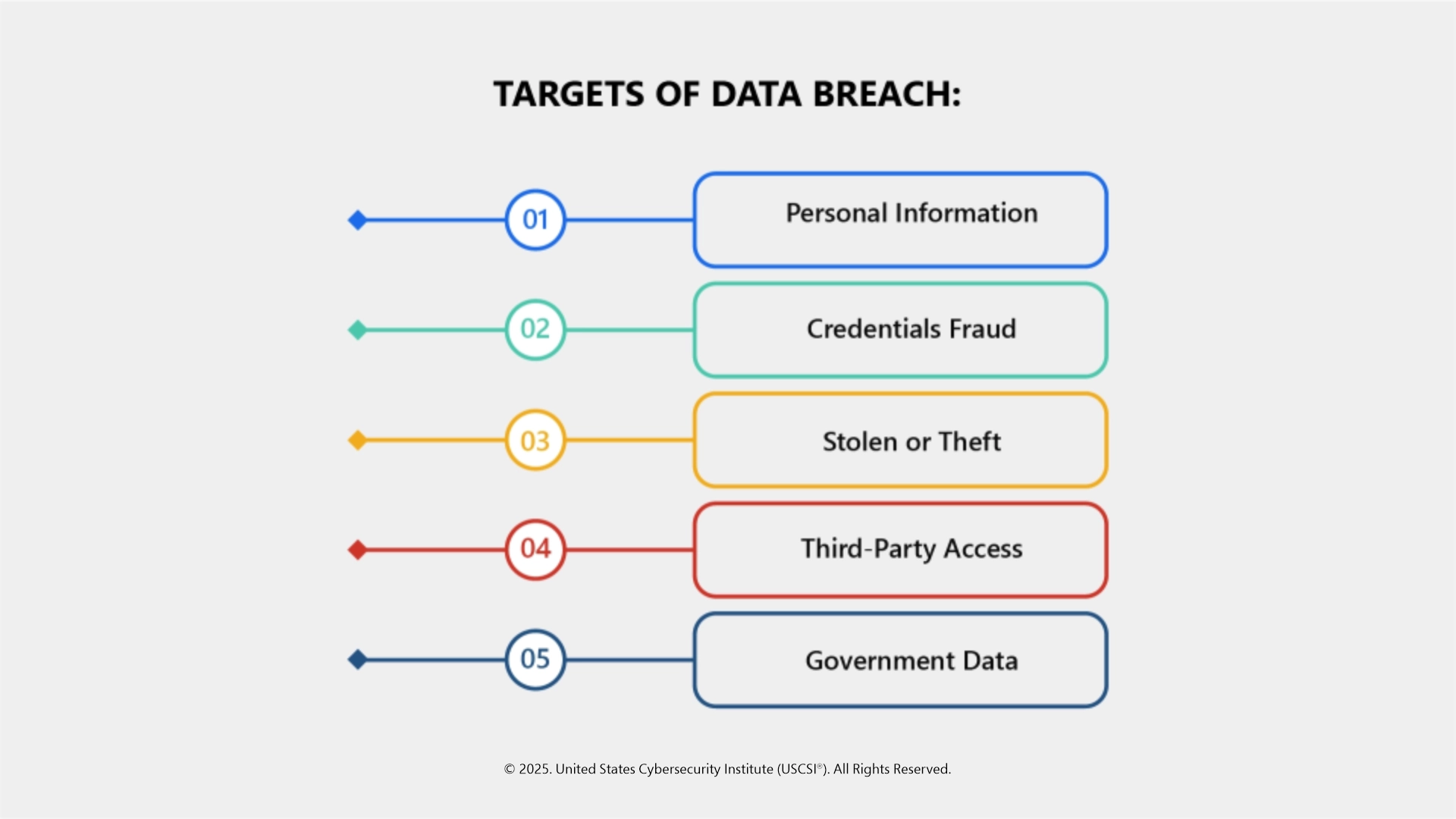
It’s not always about hackers. Sometimes a breach occurs when an employee mistakenly shares private files or a laptop is lost. Regardless of the cause, the effect is the same: private data goes where it doesn’t belong. Businesses are heavily financially damaged by, and suffer reputational harm from, data breaches. For individuals, they result in identity theft, scamming, and emotional damage.
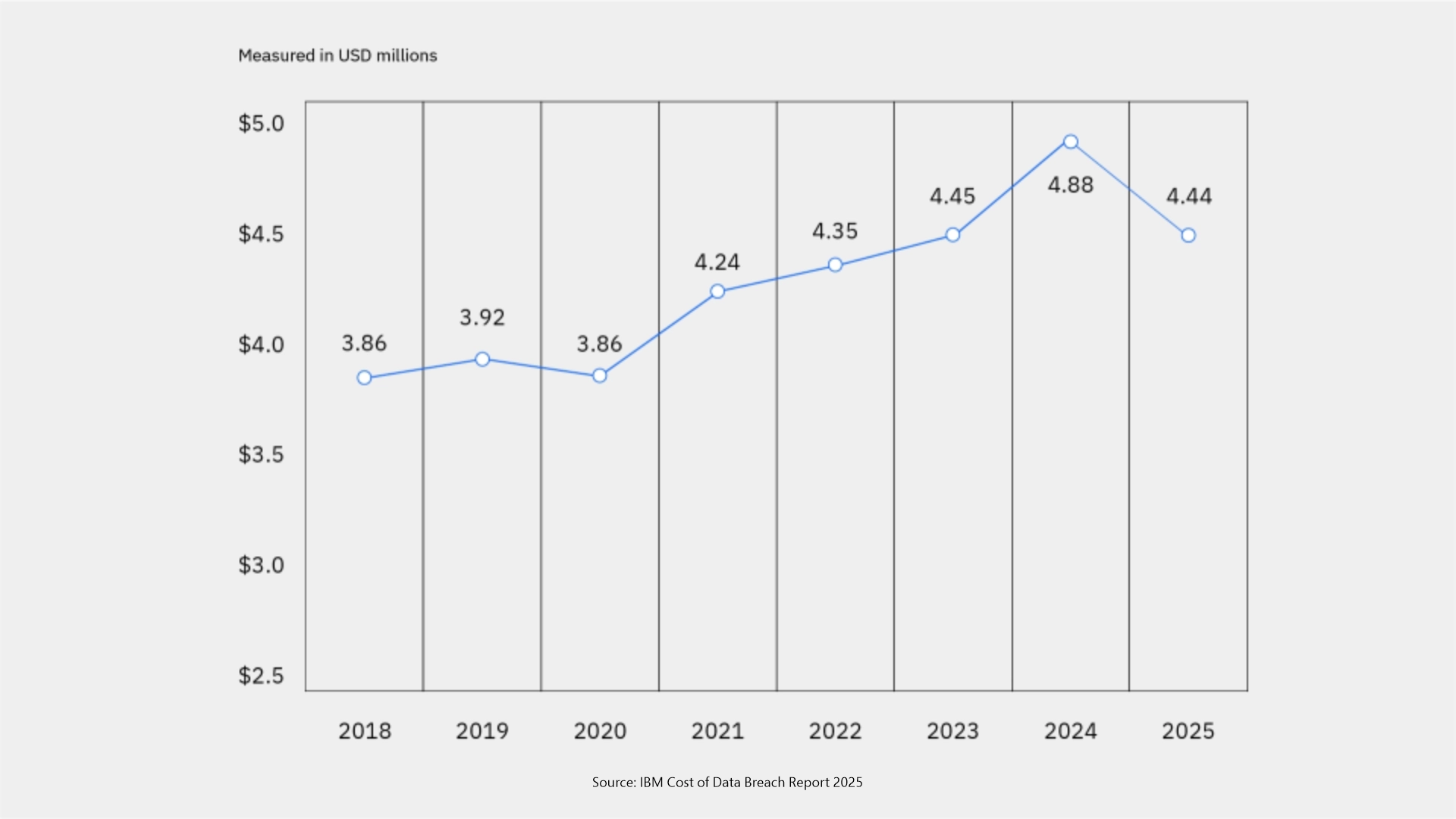
Source: IBM Cost of Data Breach Report 2025
In the graph above, 2024 has the highest cost of a data breach is 4.88 million USD. The cost reduced sharply by about 9% in 2025, and the cost of the data breach is 4.44 million USD. It is also found that 16% of data breaches involved an attacker using AI to carry out the attacks. (IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025)
Various Types of Data Breaches
Not all security violations are visible to the eye. There are different types of cyber attacks, and knowing them helps us stay protected against them. Here are a few popular types of data breaches:
- Hacking Attacks: A breach occurs when attackers figure out how to penetrate weak security.
- Phishing: False messages that dupe people into handing over login details or clicking on malicious links.
- Malware Infections: Malware gets into devices to steal or harm your data.
- Insider Threats: Employees or contractors (accidentally or on purpose) abuse access.
- Missing or Stolen Devices: Decrypted laptops, phones are risk areas.
- Vulnerable or Repeated Passwords: Weak and reused passwords make it easy to crack passwords.
These are examples of why strong security is important to organizations and people.
How Does a Data Breach Occur?
The typical data breach is committed in phases:
- Planning and Research: An attacker investigates their target to determine vulnerabilities. This could be old systems or careless workers.
- Infiltration: They initiate an attack by ways such as phishing, malware, or stolen login credentials.
- Data Exfiltration: Having made it into your system, they either copy or move sensitive data.
- Exploitation: It can then be sold, shared, or used for fraud, blackmail, and other forms of even larger cyber attacks.
By learning this process of data breach, cybersecurity experts can catch and block the strike incidentally, with the right data breach prevention practices.
Major Causes of Data Breaches
Not all data breaches are high-tech attacks. It is often due to human error or something that has been overlooked. Here are some of the culprits:
- Easy-to-Guess Passwords: Attackers can break into the system with weak passwords.
- Patch Management: Not updating software can lead to exposure of vulnerabilities.
- Human Error: Your staff can fall for malicious links or accidentally send information to the wrong recipient.
- Stolen Devices: Stealing laptops and phones becomes easily exploitable in an environment free of encryption.
- Third-Party Vendors: A contractor’s bad cybersecurity habits are often your (hidden) problem.
These ubiquitous data breach risks indicate that safeguarding your organization’s data is not solely a technological issue, but also requires awareness and training components.
Data Breach Use Cases
To understand the scope of the problem, take these examples:
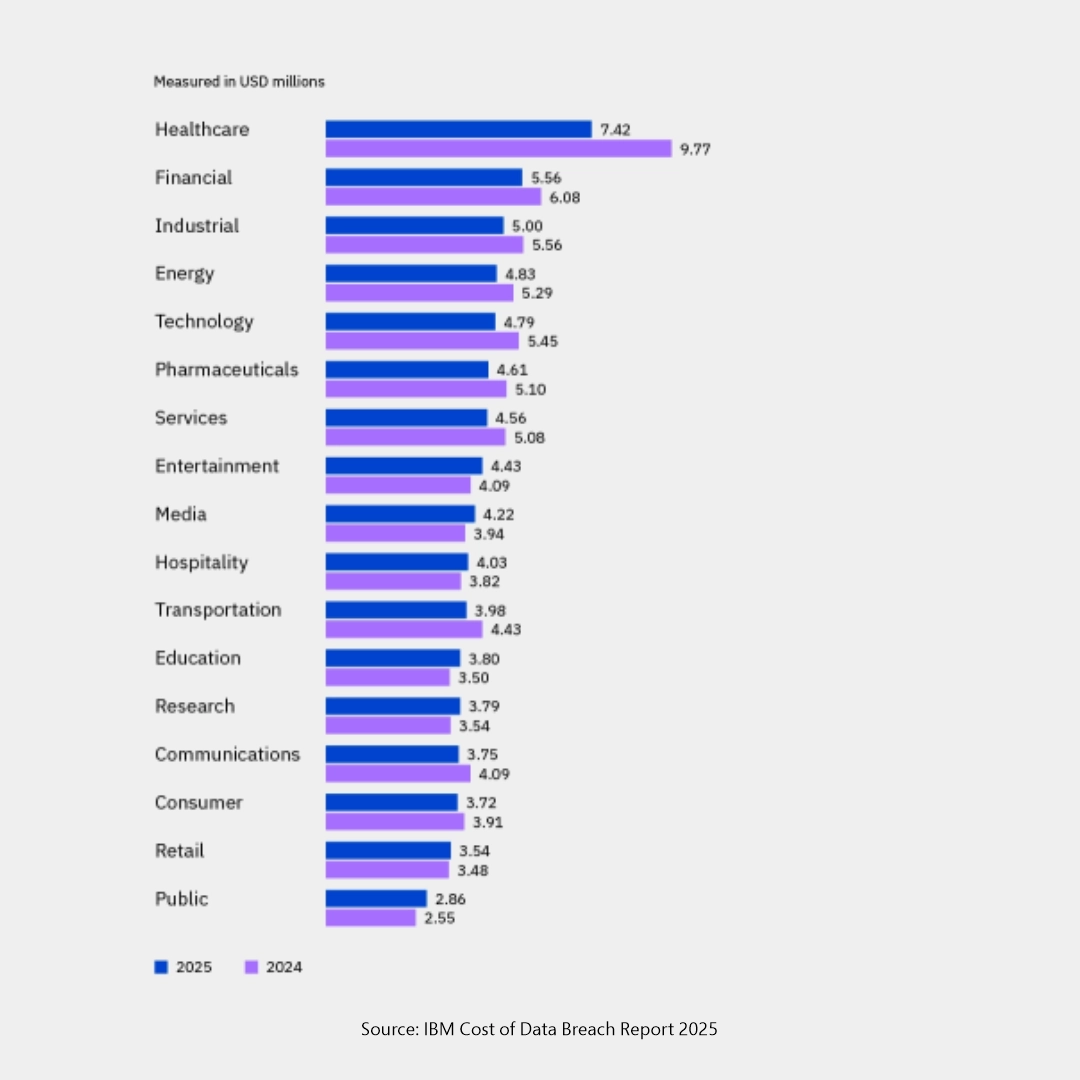
This graph is published by IBM: Cost of a Data Breach Report 2025 to show how much data breaches are affecting various sectors across the world. These examples demonstrate that no business or industry is immune to data breach attacks.
Challenges in Stopping Data Breaches
Data breach challenges, even with sophisticated tools, persist. Advances in technology, such as data crunching, have not entirely overcome most data breach challenges. Attackers are always changing their techniques, making it difficult for defenders to protect remaining assets. The surface to attack has broadened with remote work and cloud adoption. Regulations, such as GDPR and HIPAA, increase the pressure to handle sensitive data with care.
The hardest part, though, is human behavior. One wrong click can do enormous damage. This is why developing cybersecurity expertise in employees is as important as investing in technology.
Now, let’s understand the most crucial concept, which is how we can prevent these data breaches from happening with us or with our organization.
How to Prevent a Data Breach?
Here’s what an example of a coherent plan to prevent a data breach looks like:
- Use Strong Authentication: Use extremely complex and unique passwords that all should use in every account and make use of multi-factor authentication.
- Maintain Broad Systems: When the opportunity arises, update systems and systems in the organization and check the vulnerabilities of various software and systems.
- Educate Your Workforce: Training employees on the cybersecurity topic can make them aware of phishing attacks and other infiltrations as well as avoid making expensive errors. Hire the right talent by evaluating their skills and valuable cybersecurity certifications that validate their knowledge and seriousness in this field.
- Encrypt Data: Make the sensitive data unreadable without a key.
- Utilize Smart Tools: Use data breach discovery tools to spot threatening activity as fast as possible.
- Hire Ethical Hackers: Security testing by ethical hackers indicates weaknesses before attackers find and exploit them
- Prepare Incident Response: If a breach happens, having an incident response is key to minimizing the fallout.
Cybersecurity Skills and Careers
As data breaches escalate, companies are in more need than ever for skilled cybersecurity professionals. A cybersecurity certification course can help you learn how breaches work, and a certification can verify your knowledge. With a solid cybersecurity education, you will be able to specialize in areas such as ethical hacking, incident response, or risk management.
The Bottom Line
Data breaches are becoming the most serious threat. They target people, businesses, and even governments. Now you know what a data breach is, its types of attack, how they are carried out and data breach prevention techniques, you also observed data breach use cases and challenges, as well as the most effective strategies for data breach prevention.
The lesson is obvious: securing data is all of our responsibility. Companies need to create better systems, and individuals need to adopt smarter online habits. Meanwhile, there are continuing demands on cybersecurity professionals to continuously upskill and be in front of the attackers.