

Top Programming Languages to Master for Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is the fastest growing area in technology, and according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, employment of information security analysts is expected to grow 33% from 2023 to 2033, which is much higher than the national average. Threats are becoming more complex, requiring cybersecurity professionals to not only detect and mitigate risks but also to understand the systems they protect on a fundamental level. Part of the way we meet these requirements is by programming.
Programming languages are used throughout cybersecurity for many purposes, whether it is writing custom scripts to automate monitoring, dissecting malware during the reverse engineering process, or identifying vulnerabilities and exploits in a web application. From understanding which languages to purposely learn as part of one's cybersecurity career to ultimately demonstrating their applications as experts.
Now, let's examine the most relevant cybersecurity programming languages in today’s time and how each contributes to real-world applications.
Python
Best for: Automation, scripting, custom security tools
Python remains the programming language with all-around support for many cybersecurity roles. The readability of the syntax and the depth of libraries make it a great choice for automating an analyst's activities, including log/event analysis, vulnerability scanning, and developing tools. Python is also seen in pen-test and threat intelligence workflows, as it is flexible and has lower barriers to entry.
C and C++
Best for: Exploit development, system-level analysis
Because C and C++ allow direct interaction with memory and system architecture, they are essential for anyone who works professionally in malware analysis, exploit development, or operating system security.
They also enable the level of intensity required to properly analyze and understand vulnerabilities, such as the ability to perform buffer overflows and memory mismanagement, which are at the heart of common avenues for an attacker to compromise a target system.
JavaScript
Best for: Web application security testing
JavaScript is central to modern web application technology. Its wide use makes it a common attack path. Application security professionals need to know JavaScript in order to find and fix client-side vulnerabilities such as XSS (cross-site scripting), to manipulate browser behavior, and to evaluate the security of content from dynamic sources.
PHP
Best for: Securing server-side web applications
PHP remains a very popular language for server-side development, as it continues to be used to power an array of platforms, including WordPress, Drupal, and many legacy applications. Because of its widespread use and history of vulnerabilities, PHP tends to be a prime target in web-based attacks.
Applications in cyber security:
- Auditing insecure PHP code to identify vulnerabilities such as code injection or file inclusion
- Identifying outdated or misconfigured CMS platforms
- Writing secure scripts and testing server-side logic
SQL
Best for: Database security and injection prevention
SQL is still one of the most attacked elements in enterprise systems, mostly through injection attacks. For cybersecurity experts, familiarity with SQL assists in auditing queries, identifying suspicious data behaviors, and defending against SQL injection, one of the most persistent web security threats. SQL is also important when performing security assessments of data-driven applications.
Bash and PowerShell
Best for: System scripting, automation, and response
For scripting at the system level, you can't beat Bash or PowerShell. Bash is the go-to scripting language in Unix/Linux environments, while PowerShell is the primary language of choice in Windows-based networks.
Both languages are extremely powerful when it comes to automating forensic analysis, patch management, system audits, and several components of incident response in cybersecurity. Because of their ability to automate system-level tasks, security professionals have great implementation capabilities to control system-level defenses.
HTML
Ideal for: Understanding web structure to find markup-based vulnerabilities
Although there is no programming logic in HTML, e.g., loops or conditionals, it's still the basis for how websites are created and rendered. Understanding HTML allows cybersecurity professionals to recognize vulnerabilities that can occur from poor structure or malicious markup.
Assembly
Best for: Reverse engineering and binary analysis
Assembly language sits at the bottom of the programming language hierarchy, meaning it requires a level of expertise few will ever develop, but in return, it provides valuable insight into how software operates at the machine level.
Assembly isn't an everyday language, but it's valuable for reverse engineering, malware analysis, and exploit research. It helps uncover advanced threats and decode obfuscated malicious code.
Other Key Emerging Programming Languages
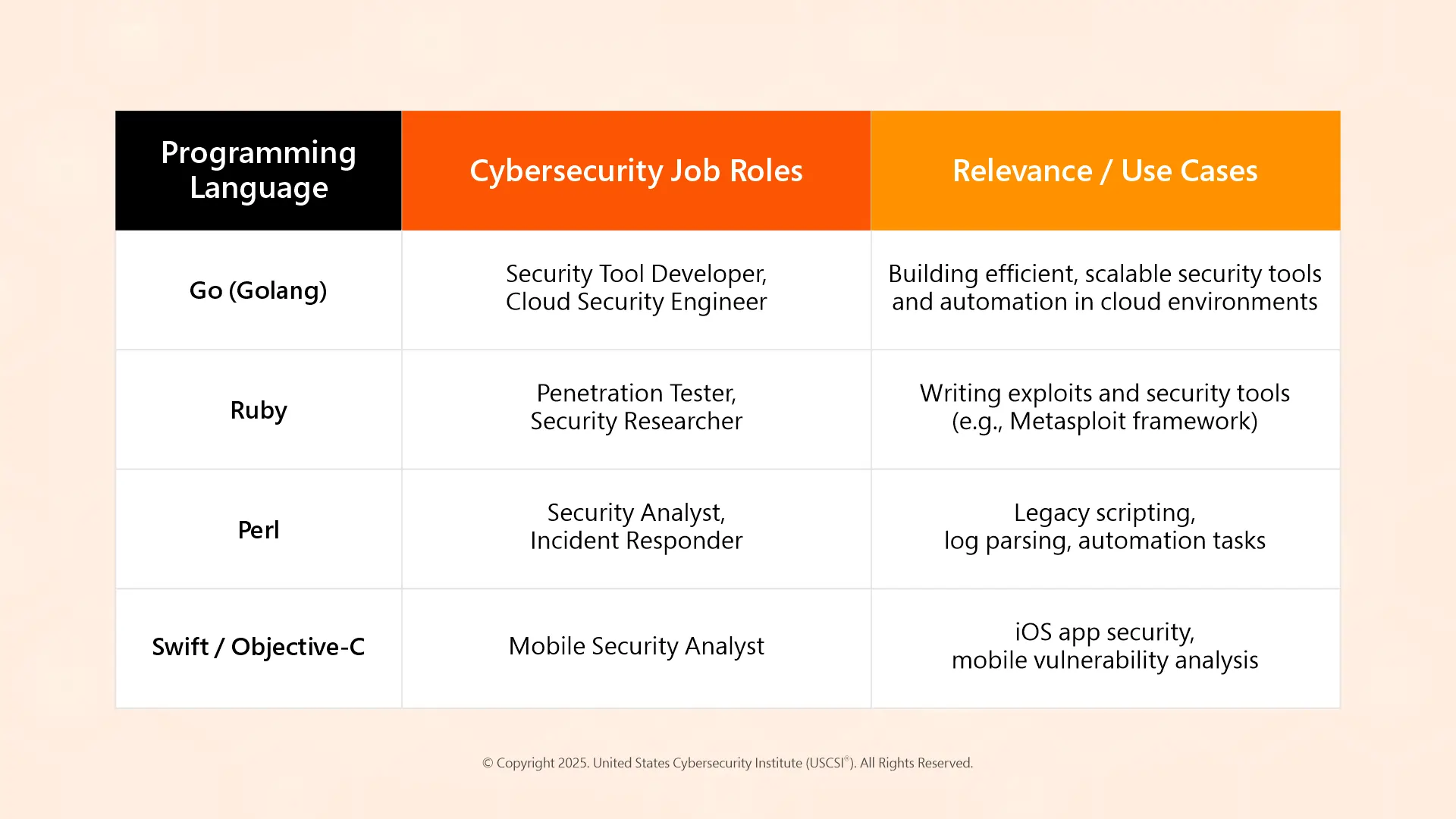
How Programming Languages Are Used in Cybersecurity
Each part of the cybersecurity field utilizes programming in different ways:
- Malware analysts use C, Assembly, and Python to analyze malware and extract indicators of compromise.
- Pen testers use Bash, PowerShell, and Python to build custom exploits.
- Web security uses JavaScript and SQL to evaluate both the client-side and server-side behavior.
- Defensive security uses Go and scripting languages to build cybersecurity tools and automate incident response.
If practitioners understand the intended use of each language, they can determine which ones to use and learn for cybersecurity jobs, based on their specialization.
Conclusion
Programming is central to cybersecurity, enabling specialists to automate responses, test systems, build tools, and find vulnerabilities. These languages help cybersecurity specialists think critically, respond quickly, and defend effectively in a rapidly evolving digital threat landscape.
With the demand for programming-skilled professionals ever-growing, upskilling cybersecurity talent with practical programming knowledge is essential. USCSI® (United States Cybersecurity Institute) has top cybersecurity certification programs to help people develop the needed technical know-how in security today, positioned to enable professionals not only to deal with the threats of today but also the threats of tomorrow.





