

Data Science and Cybersecurity: Applications, Roles, and Trends
Today, every business relies on data, predictive models have exploded because of it, and cloud analytics is a data collector. But with the rise of data and analytics comes the rise in risk. Breaches, ransomware, data leaks, and compromised AI models are now part of our regular headlines.
The PwC 2025 Global Digital Trust Insights report found that more than half of global organizations experienced major breaches last year and cloud vulnerabilities are consistently one of the top cybersecurity concerns. This finding clearly demonstrates the increased demand for smarter data-driven defense strategies that can keep up with emerging digital threats.
Businesses are now merging two essential disciplines—data science and cybersecurity. The discipline defined as Cybersecurity Data Science, utilizes data to create a layer of protection that predicts, prevents, and defends against cyber threats before they happen. Let’s explore more about this convergence.
Understanding Cybersecurity Data Science
Cybersecurity Data Science involves applying data science techniques, such as machine learning, predictive analytics, and processing big data, to detect, deter, and minimize security incidents.
It is much more than simply monitoring a system. It incorporates learning patterns over time, recognizing anomalies, and altering itself whenever a new type of attack evolves. Think of it like a self-learning system, working at the speed of analyzing millions of events a second, while identifying anomalous login attempts, predicting breaches, and alerting an analyst before any harm is done. That is the purpose of cybersecurity data science.
In summary: Data Science gives us intelligence reporting anomalous patterns hidden in giant datasets. Cybersecurity gives you security to keep those insights and systems safe. Together, it is a smarter and more proactive defense in a threatening landscape.
Why It Matters More Than Ever
Traditional security mechanisms, such as firewalls and antivirus programs, were built for a simpler, more stable world. Today’s reality is much more blurry: remote work, multi-cloud architectures, AI models, and web-based workloads have all substantially increased the attack surface of most organizations.
Cybersecurity is now everyone’s job, not just those in the boardroom or IT department. Even the tools of data science, machine-learning models, APIs, and training data, are now in the canon of hackers. Hackers have also proliferated in their attacks, leveraging AI to conduct quicker and more targeted attacks, and businesses rely on AI to protect their institutions.
Hence, the boundary between “data science” and “cybersecurity” is completely blurred. If organizations want to safeguard the future of data, they must master both.
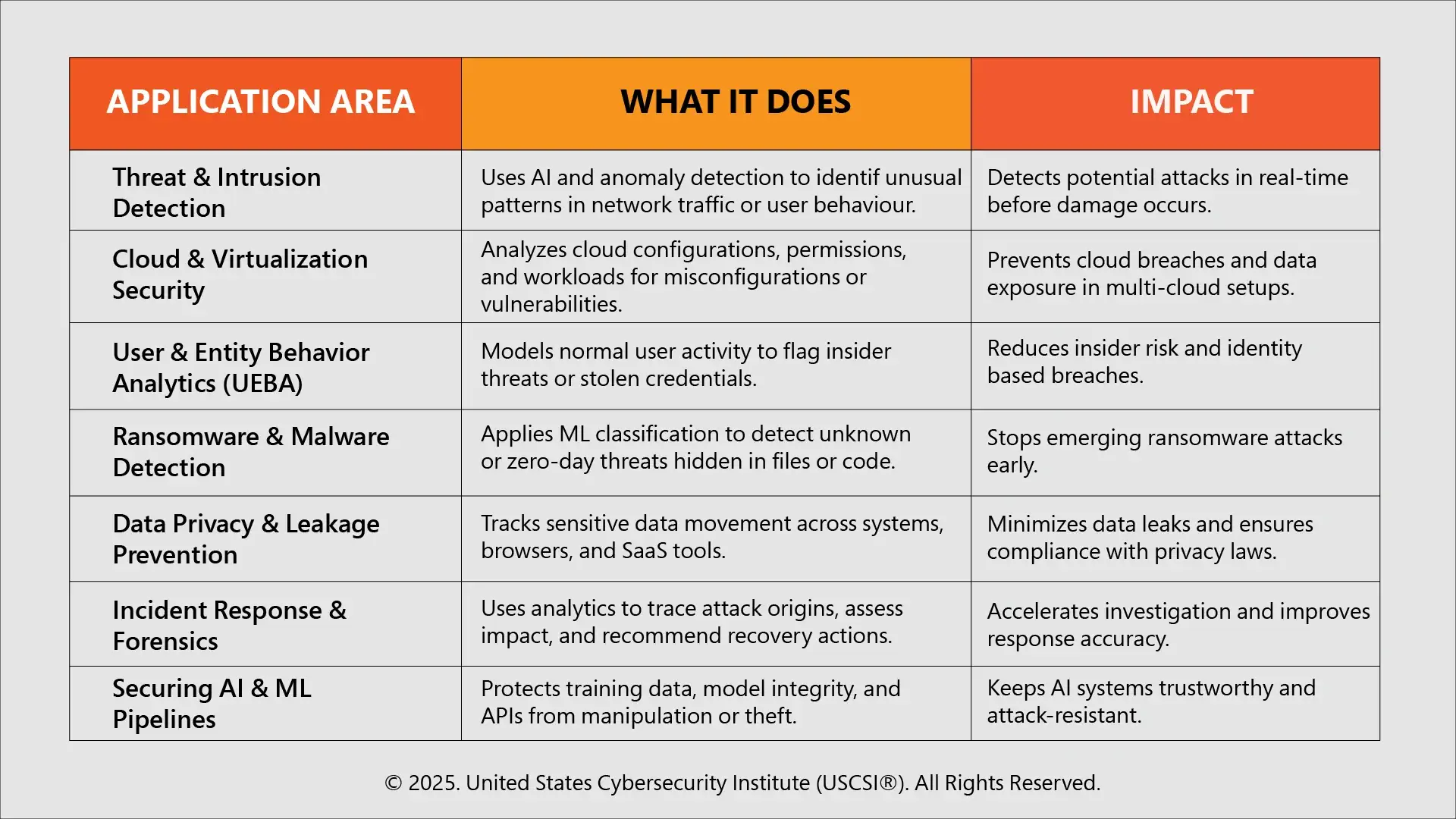
Key Applications of Cybersecurity Data Science
Cybersecurity Data Science is already in use. It powers some of the most sophisticated protective systems of the present day. Here are seven key areas of application that illustrate how this field is transforming the future of data protection:
Skills and Tools You’ll Need
With the expansion of Cybersecurity Data Science, professionals are increasingly integrating analytical competencies with traditional security disciplines to develop hybrid skill sets.
- Machine Learning and AI: for anomaly detection, classification, and prediction in behavior.
- Big Data Analytics: to analyze and manage the multitude of logs, network telemetry, and event data in the cloud.
- Programming Languages: /python/, /r/, and /sql/ for data wrangling and building models.
- Cybersecurity concepts like encryption, zero trust, indicators of compromise, and vulnerability assessment.
- Cloud computing skills for securing workloads within AWS, Azure or GCP.
Important tools are:
- Security Analytics Solutions (SIEM, SOAR, UEBA) for ingesting and analyzing threat data.
- Data Security Tools to Monitor and Control Sensitive Data (data loss prevention, cloud-access brokers)
- Visualization dashboards like Power BI, Kibana, Grafana for data to inform an educated threat perspective.
Emerging Roles in the Field
As the intersection of Cybersecurity with Data Science advances, new niche roles are emerging:
- Security Data Scientist—uses advanced analytic tools to create predictive models for cyber threat detection.
- Cloud Security Analyst—leverages data-driven monitoring and risk assessment to secure organizations’ multi-cloud environments.
- Data-Driven Cybersecurity Consultant or Advisor—provides counsel to organizations on how to utilize data to inform and transform their security program from a reactive strategy into a proactive strategy.
- AI Security Engineer—tasked with protecting the security of machine-learning systems and anything AI-related that involves sensitive data.
- Senior Data Scientist (Cyber Security Focus)—is equipped with advanced statistical modeling capabilities, along with extensive knowledge of the cyber threat landscape.
Cybersecurity in the Cloud and Browser Era
As employees perform work across both CRM systems and cloud applications, the browser has become the new perimeter of security and has the ability to put sensitive data at risk from unsecured extensions or other invisible leaks.
Cybersecurity in Data Science incorporates analytics at the data source, even as far back as the browser, endpoints, and cloud applications. It provides real-time monitoring of activity to identify abnormal file transfers, unwanted behavior, or risky behavior while automatically enforcing security policies to avoid breaches.
Meanwhile, cloud analytics track configurations, access, and API use to detect anomalies, ensuring continuous, proactive protection as data moves between browser and cloud.
Merging Cybersecurity with Data Science: Trends Toward 2026
- Data-Centric Protection—Security measures now focus on the protection of data wherever it travels, not just the protection of the data behind the network perimeter.
- Zero-Trust Cloud Environments—Identity and behavior verifications are now employed dynamically instead of static access control on cloud platforms.
- Browser-Level Security—The monitoring and securing of all browser activity is now the method to ensure that users are interacting with their cloud applications and data securely.
- Adversarial Data Defense—Protect models, datasets, and analytics pipelines from changes or corruption.
- Unified Cyber-Digital Teams—Data scientists and cybersecurity specialists will aim at delivering common operational objectives as team members focused on predictive security.
Know more about Top 8 Cybersecurity Trends to Watch Out in 2026
Why This Integration Is Essential
The benefits of cybersecurity data science go beyond just protecting organizations against threats. It enables safer innovation. It allows organizations to more easily adopt cloud computing, AI, and automation without worrying about unknown vulnerabilities.
There are also cost efficiencies, as better analytics means less time to manually investigate and fewer missed alerts. Most importantly, it creates trust with customers, regulators, and employees that the data used for innovation is genuinely secure.
Conclusion
Data science and cybersecurity are reshaping how organizations protect their digital assets. Combining data science, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity allows for predictive defense that changes as quickly as modern threats.
To keep up in this rapidly changing environment, professionals will need to reskill continually. Earning globally recognized cybersecurity certifications from USCSI® will equip professionals with the analysis and cybersecurity skills necessary to meet future challenges.
The future of data protection is not in cyber but in intelligence that is proactive, adaptive, and powered by cybersecurity data science.





