The Rising Cyber Risks of IoT and How to Stay Secure
The Internet of Things is changing how we live and work in a connected world of billions of devices across the globe, from smart home devices to entire manufacturing plants to medical devices. In a 2025 report from Statista, the number of predicted IoT devices will increase to over 35 billion worldwide by the end of the year; we can see that this number is rapidly growing. The convenience of IoT-connected devices creates a connected world but comes with increased, potentially disruptive, cybersecurity risks to one's life, business, or critical infrastructure.
As the number of devices increases, the sophistication of cybersecurity threats increases in step with the advancement of IoT and any associated risks to security, including AI-driven attacks, insecure devices resulting in Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) that endanger infrastructure, and changing hacking methods. In an ever-connected world, organizations and cybersecurity professionals need to understand the threats that exist and how to protect against them.
Why IoT Is a Prime Target for Cybercriminals
Every IoT device can be an entry point for attackers. Many have minimal security, like default passwords, outdated firmware, and weak authentication, due to cost and speed pressures. The lack of universal security standards leads to inconsistent protection, leaving many devices vulnerable.
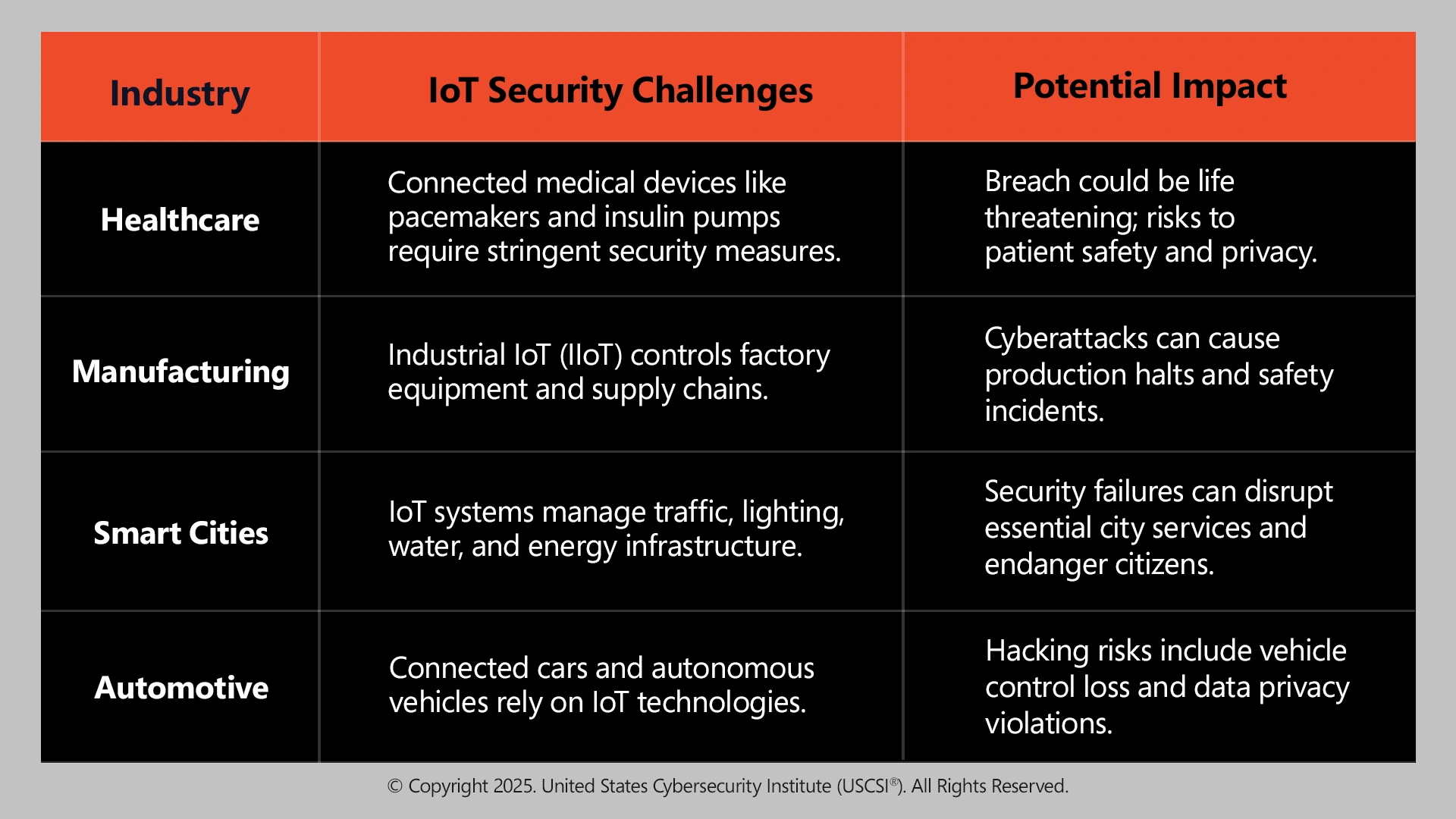
Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, energy, and smart cities utilize various levels of dependence on IoT. There are, therefore, potentially significant consequences due to breaches within Health and Safety, Financial, Environmental, or social domains, which makes IoT security a global priority.
The Role of AI in Cybersecurity and Cyberattacks
Artificial Intelligence is a double-edged sword in the world of cybersecurity and IoT. On one side, AI allows security teams to analyze vast data streams from IoT devices, recognize anomalous actions, and rapidly react to detected threats. AI-powered security solutions streamline threat hunting, behavioral analysis, and incident response, enabling organizations to defend vast IoT environments more effectively.
On the other hand, cybercriminals also use AI to launch more sophisticated attacks. AI can scan networks of vulnerable devices rapidly and adapt attacks to evade detection. These AI threats include automated phishing, polymorphic malware, and AI-driven reconnaissance that evolve faster than traditional defenses.
Because of this, cybersecurity specialists must keep upgrading their skills through targeted cybersecurity training programs to stay ahead of new threats.
DDoS Attacks and IoT Botnets: A Growing Concern
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks seek to disrupt their target's service by inundating their servers with unmanageable amounts of traffic. IoT devices have become a critical component of the attacker's toolkit for building botnets, which are large networks of hijacked devices used to deliver large-scale DDoS attacks.
The Mirai botnet attack in 2016 was a wake-up call. A huge number of insecure IoT devices, including cameras and routers, were taken over in an attack that was one of the biggest DDoS attacks on record. DDoS attacks of this nature have escalated since then in size and frequency.
In 2025, we can see that DDoS attacks continue to utilize IoT botnets, making the case for better security for these devices as well as security against a potential compromise at the network level.
Sector-Specific Challenges in IoT Security
How Consumers Can Protect Their IoT Devices
Securing IoT devices is not solely a responsibility of manufacturers and enterprises. Consumers also play a crucial role:
- Change default passwords immediately after setup, and create strong, unique passwords.
- Stay on top of any available firmware and software updates that address vulnerabilities.
- Do not connect IoT devices to unsecured public Wi-Fi networks.
- Turn off unused features or services on devices that contribute to an increased attack surface.
- Use network segmentation, such as separate Wi-Fi networks only for IoT devices.
The Growing Demand for Cybersecurity Specialists
The growth of IoT threats leads to a growing need for cybersecurity professionals who can work in this specific space and for experts who can architect, implement, and manage security systems for IoT.
If you are considering a career in IoT cybersecurity, you'll need an understanding of:
- Network security fundamentals
- IoT communication protocols and standards
- AI-based threat detection and response
- Incident response and recovery planning
Organizations are also encouraging employees to obtain a certification in cybersecurity.
For professionals looking to specialize in the IoT security area, the top cybersecurity certifications, like Certified Senior Cybersecurity Specialist (CSCS™) certifications from the United States Cybersecurity Institute (USCSI®), address many of the emerging threats to IoT, including vulnerabilities, as well as defense techniques that provide candidates with hands-on skills to ensure the overall protection of IoT environments.
Regulatory Landscape and Industry Standards
Governments and regulators know the importance of IoT security. Current law and standards like the U.S. IoT Cybersecurity Improvement Act, the European GDPR (which affects the data privacy of connected devices), and subsequent winner findings from groups like NIST will shape the future of IoT security.
While attempting to comply with these regulations, it is important to encourage manufacturers and organizations to adopt more robust security practices.
The Future of IoT Security
The Internet-of-Things ecosystem will continue to expand as technologies like 5G and edge computing will provide new connectivity and data flow opportunities. This will continue to expand the attack surface and complexities in defending these networks.
The cybersecurity industry will need to continue to adapt by utilizing AI and other forms of automation and developing a workforce that understands the new threats that are emerging regarding IoT. It will become essential to continue professional development and certification.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things (IoT) introduces unprecedented connectivity and innovation, but it also brings evolving cybersecurity challenges. AI-driven attacks, DDoS botnets, and vulnerabilities unique to specific sectors threaten organizational resilience, demanding proactive and strategic responses. By continuously learning and leveraging trusted resources, professionals can stay informed about their role in protecting the IoT ecosystem and help build a secure, sustainable digital future.