

The Silent Thief: Understanding and Combating Cryptojacking
Not just data, devices, or applications but cyberattacks can also compromise your computing resources. The world of cybersecurity is huge, and this Cryptojacking threat is particularly an insidious practice aimed at exploiting the computing resources of individuals and organizations.
While other cyber-attacks, like ransomware in which attackers demand ransom for data recovery, cryptojacking is a silent technique to hijack your computing resources to mine cryptocurrency without ever being identified by the owner.
This attack can also have a significant impact as it can drain your system’s performance and raise your electricity bills as well as damage your systems in the long run without you being aware of what’s happening behind the systems.
Let us understand this unique kind of cyberthreat in detail and learn how to protect our systems from unauthorized access and use.
What is Cryptojacking?
Cryptojacking, often referred to as cryptomining, is a cybercrime where criminals get unauthorized access to someone else’s computer, smartphone, tablet, or even servers to mine cryptocurrency.
This is done by injecting malicious code into websites or distributing it through phishing emails and infected software. This code then exploits the victim’s computing resources, including processors and storage, to solve complex mathematical problems, which is an important step in generating new cryptocurrency units.
The mined coins are then transferred to the attacker’s digital wallet, and the victim is left with nothing but a sluggish device and an increased electricity bill.
How Does Cryptojacking Work?
The Cryptojacking attack basically involves three steps:
- Infection
- Mining Operation
- Profit Transfer
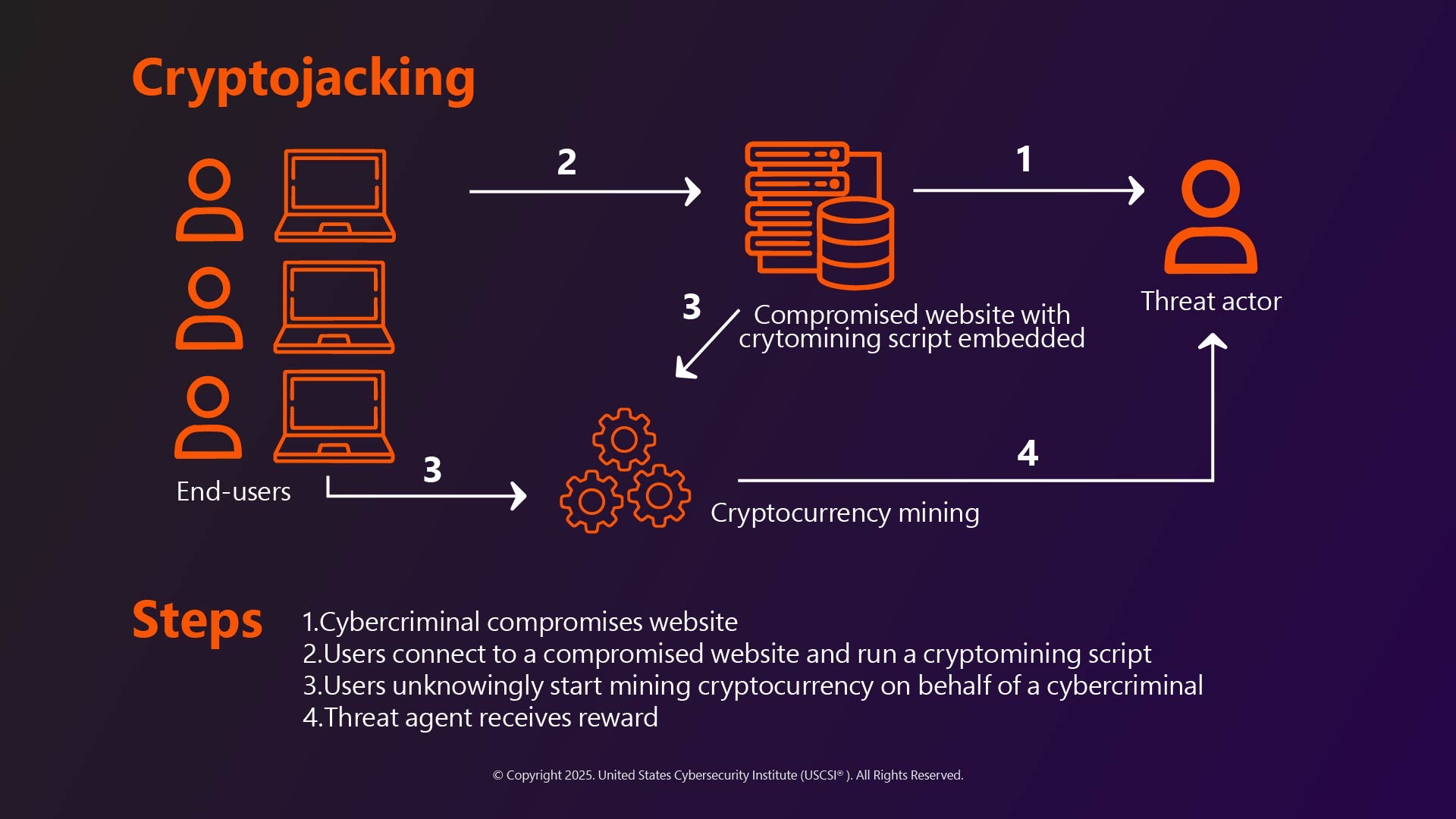
Let’s understand them in detail.
- Infection
The first step is getting into a system. This can be done in several ways. For example, website injection. In this, attackers inject JavaScript code into websites when a user visits an infected site where the script executes in their browser. Then, it uses its systems to mine cryptocurrency. This phenomenon is called ‘drive-by-cryptomining. ’
Another way to infect a device is Cryptojacking malware, which is often disguised as legitimate software or can be attached to phishing emails. So, if the user downloads or opens it, the malware installs itself on the device and starts mining operations.
Often, hackers can gain access to compromised systems and vulnerable servers or cloud infrastructure where they install mining software directly.
- Mining Operation
The next step followed by infection is mining. The malicious codes use the victim’s CPU and even GPUs (in some cases) to solve cryptographic puzzles. As the mining processes are run in the background, disguised as legitimate system processes, it becomes difficult for users to detect such threats.
The intensity of the mining operations can also vary depending on the attacker’s requirements and the system resources of the victim.
- Profit Transfer
Finally, the mined cryptocurrency is sent to the attacker’s digital wallet, who can then convert them into other cryptocurrencies or traditional currencies.
Why Is Cryptojacking a Serious Threat for Organizations?
Cryptojacking can turn out to be fatal for organizations if they run for a long time without detection. Unauthorized cryptomining silently drains CPU resources, which leads to poor performance of victim’s systems and even damage them if they are used constantly.
It possesses a worm-like nature through which it can spread across networks and create its own network of mining nodes. Thus, it leads to an increase in the overall attack surface and makes it difficult to remove, also increasing the overall harm to the organization’s infrastructure and operational cost.
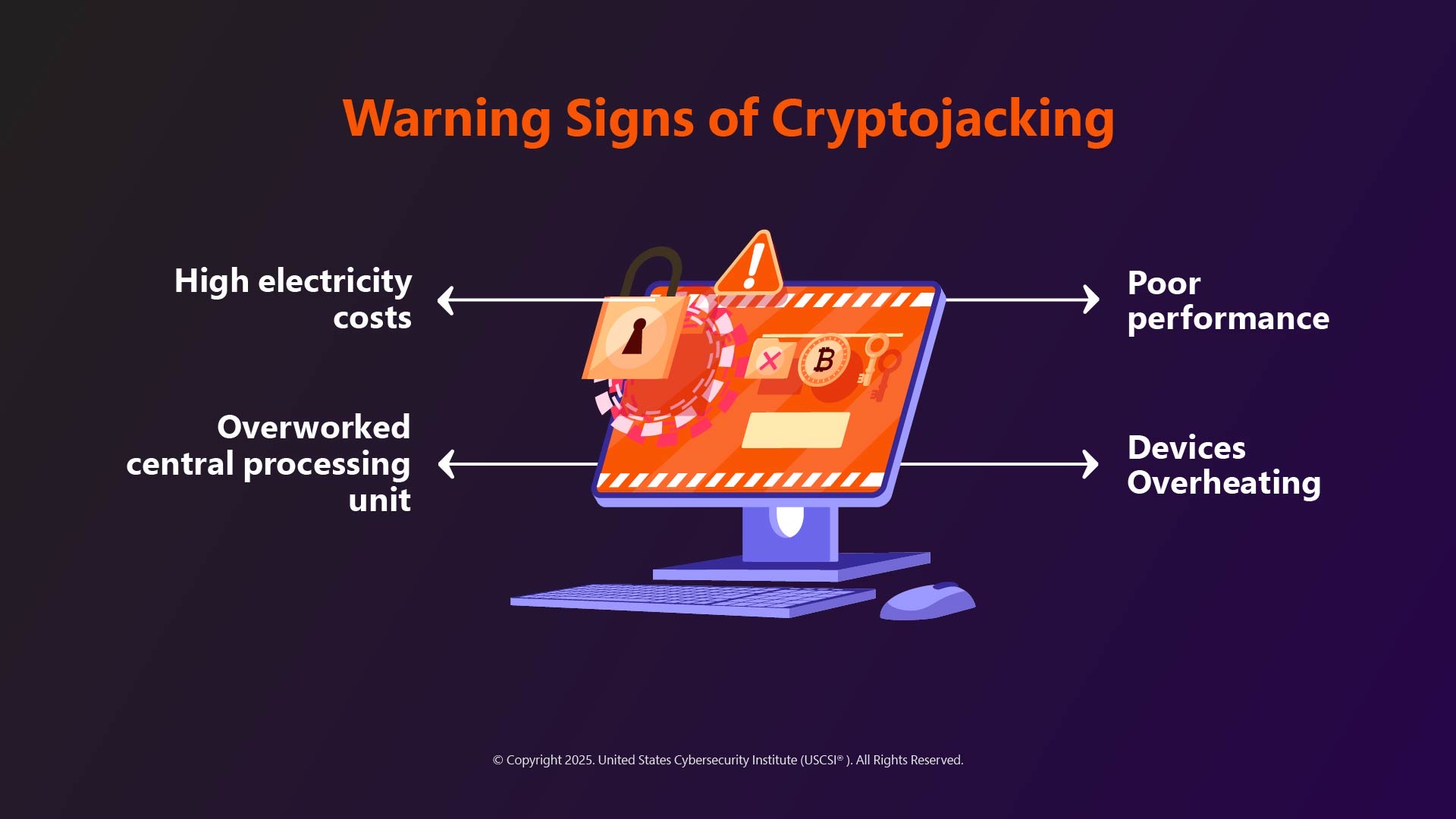
The Impact of Cryptojacking
Though it doesn’t sound dangerous, as no data or sensitive information are compromised in these types of attacks, they can have significant consequences for organizations, such as:
- Degradation in performance – Mining operations utilize a lot of resources, including CPUs and GPUS, which leads to heavy slowdowns in system performance. Applications can become unresponsive, and tasks will take longer time to complete.
- Higher electricity bills – cryptomining also requires huge amount of electricity for its operations. So, victims will get a high electricity bill without any clue of why it’s happening.
- Damage to hardware – Constant utilization of resources and intensive mining can lead to overheating of hardware components and early damage of the system.
- Reduced battery life – Cryptomining drains the battery of compromised devices (laptops, smartphones, tablets) quickly.
- Security risks – Cryptojacking malware can also lead to opening backdoors for other cybercriminals to install additional malicious software or steal data
In the long run, these costs can be significant for organizations. Organizations must therefore train and educate their employees with knowledge of cryptojacking and their prevention strategies. Offering them cybersecurity certifications and courses can help them gain the required knowledge to protect against not just cryptojacking but also attacks like phishing emails, social engineering, etc.
Types of Cryptojacking
Let us now briefly discuss the types of Cryptojacking techniques.
- Browser-based Cryptojacking
It refers to malicious JavaScript code that can be injected into websites and use the visitor’s browsers to mine cryptocurrency when they browse. Since no files are downloaded, it can become difficult to detect them
- Binary-based Cryptojacking
Attackers deploy executable files that may seem legitimate, but upon installation, the miners can run as independent processes. These miners persist through system reboots and can also directly access the hardware.
- Supply-chain Cryptojacking
In this type, mining code is embedded into software packages or updates through compromised distribution channels, and they can automatically deploy with legitimate software installations.
- Fileless Cryptojacking
This is another type of Cryptojacking where the mining code works within the system memory by using tools like PowerShell to avoid writing files to disk and thus become very difficult to identify.
- Cloud Infrastructure Cryptojacking
Here, the attackers exploit cloud resources that are not properly configured for security or those that have weak credentials to deploy miners in cloud environments. This makes them easier for attackers to scale rapidly by incorporating additional resources.
Protecting Yourself from Cryptojacking
Though Cryptojacking is hard to identify, there are some ways you can prevent being infected with Cryptojacking malware.
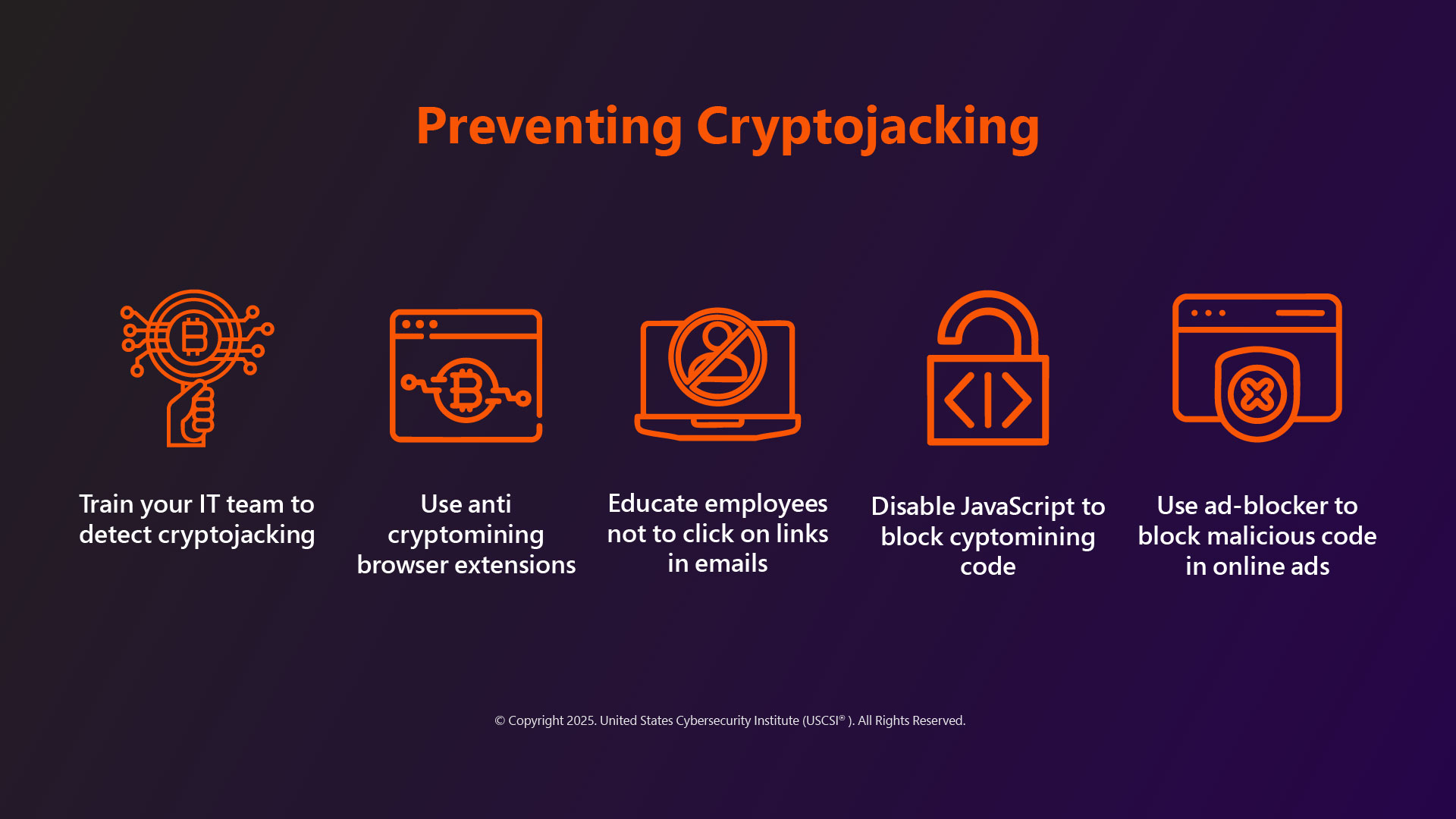
Here are a few things to consider:
- Install Ad Blocker – there are several ad blockers that you can use to detect and block Cryptojacking scripts embedded in websites
- Using reputed anti-malware software – Users should install and use reputable anti-malware software that can effectively detect and remove such malware
- Always update software – keep your operating system, web browsers, and other software updated to patch security vulnerabilities
Apart from these, there are other cryptojacking detection techniques and prevention strategies. Beware of suspicious and phishing emails, monitor your device’s performance, and if you find it unusually slow or lagging, check CPU usage and perform the corrective measures. Employing browser extensions can also help contain and block Cryptojacking scripts. There are a few vendors who also offer specialized anti-cryptojacking software to detect and block cryptojacking.
With proper awareness, corrective measures, and essential cybersecurity tools, you as an individual or an organization, can effectively detect, block, and eliminate cryptojacking.
Summing up!
Cybercriminals try to find every way to exploit users and organizations, and cryptojacking is one of them. Therefore, staying vigilant and implementing robust security measures can help them protect against these silent thieves. You must understand the risks and take proactive steps to minimize your exposure to cryptojacking and keep your systems safe and protected from these innovative cyberattacks.





