All About Prompt Hacking and Ways to Safeguard Your AI Systems
In today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, Prompt Hacking has emerged as a critical concern, particularly with the growing adoption of Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. According to Check Point’s AI Security Report, 1 in 80 generative AI prompts exposes sensitive data to attackers. These AI models are designed to understand and generate human-like text, enabling automation in customer service, content creation, code generation, and more.
However, their ability to process natural language inputs makes them vulnerable to attacks that exploit the trust these models place in user-provided prompts. Prompt Hacking involves the deliberate manipulation of inputs to AI models to make them perform unintended actions. Unlike traditional cyberattacks targeting software, prompt hacking exploits the AI’s decision-making logic, introducing unique challenges for organizations handling sensitive tasks.
What is Prompt Hacking?
Prompt Hacking is when attackers manipulate the inputs to LLMs to generate responses that are not intended or that are malicious, such as revealing sensitive information or circumventing content moderation. Unlike traditional attacks, this is different because it takes advantage of the AI's inherent trust in user prompts, which builds a new vulnerability that may not be caught by standard security tools.
The Rise of Prompt Injection Attacks
A common type of prompt hacking is referred to as Prompt Injection, in which adversaries inject malicious instructions into an otherwise benign prompt. With these injections, the adversary is able to change the behavior of the model, leading it to perform unauthorized actions without the user's awareness.
For example, scholars have shown that GPT-4 could be deceived into generating unsafe responses by including certain instructions in the input prompt. These prompt injection attacks signal the need for careful oversight of AI inputs and outputs and to safeguard against manipulation.
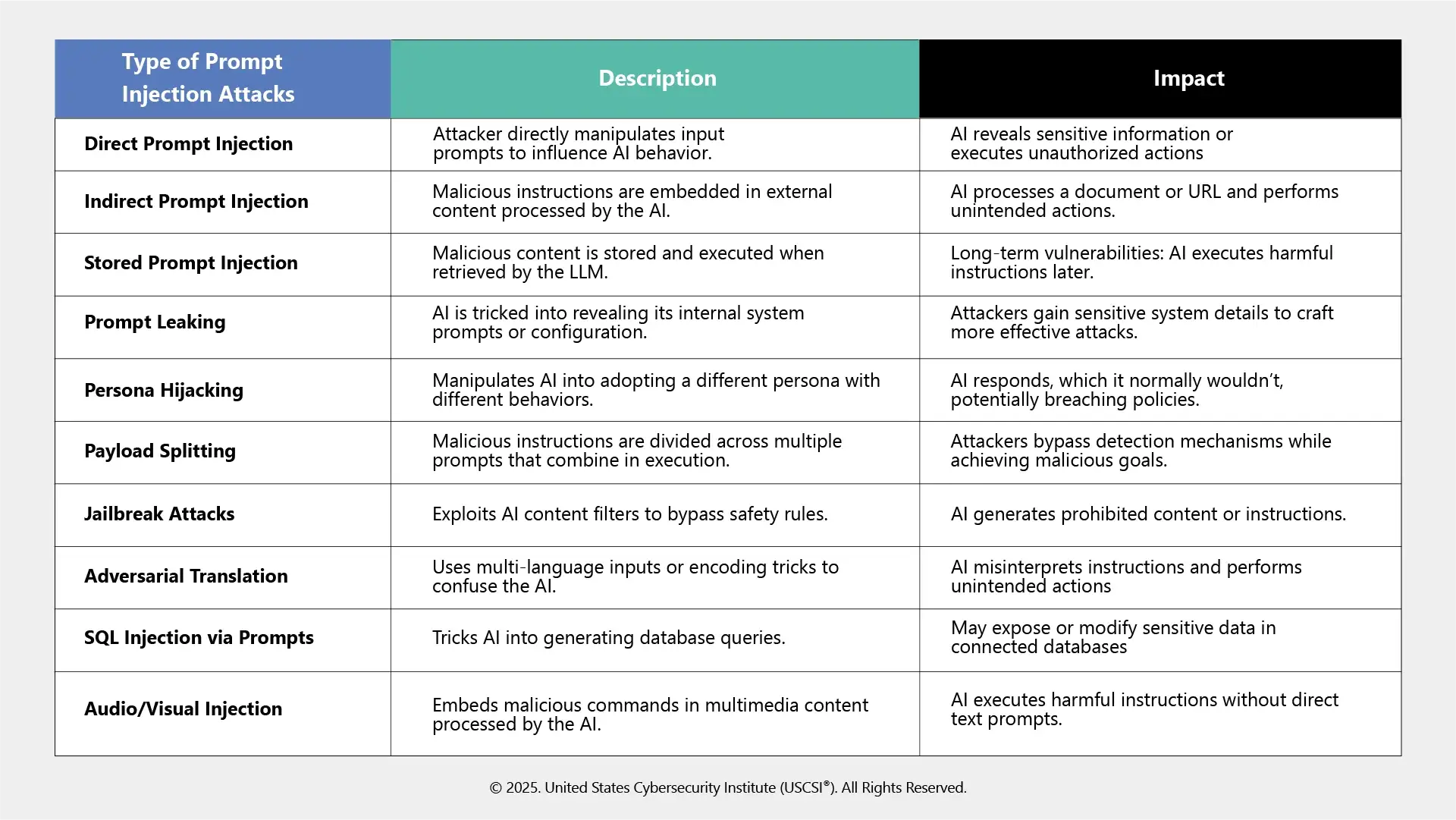
Types of Prompt Injection Attacks
Prevention requires an understanding of the different kinds of attacks. The following are the most typical kinds of prompt injection attacks:
Real-World Developments in Prompt Hacking
The following well-known instances highlight the practical consequences of prompt hacking:
-
ShadowLeak Vulnerability in ChatGPT (2025)
In terms of ChatGPT security, the ShadowLeak vulnerability illustrates a zero-click, server-side flaw found in ChatGPT's Deep Research agent, which permitted attackers to extract sensitive information from OpenAI servers with no user interaction. This demonstrates that prompt-related issues can reveal sensitive information without any type of phishing or malware infection occurring.
-
MalTerminal Malware
MalTerminal, which employs GPT-4 as a virtual assistant to create malicious code, has been developed by hackers. MalTerminal can generate real-time encryption ransomware or a Python reverse shell with the user's specific target in mind. It illustrates how prompt manipulation could empower cyberattacks indirectly.
-
Google Calendar Exploit
Researchers showed that hijacked Google Calendar invitations could be used to take over ChatGPT's Gmail connector. The AI model processes these malicious inputs and generates responses that provide access, demonstrating risk from integrated AI services.
The fact that prompt hacking is currently being used to alter data, create malware, and take advantage of AI-driven workflows demonstrates that it is not just a theoretical concept.
Preventing Prompt Hacking Attacks
To protect themselves from timely, prompt hacking attacks, organizations need to implement a multi-layered strategy that incorporates both technical safeguards and human knowledge.
Input Filtering and Sanitization
Establish comprehensive input validation and sanitization processes to identify and neutralize dangerous prompts before they reach AI systems. This includes rejecting prompt hacking attacks with patterns of behavior that are suspicious, such as inputs with strange characters or commands designed to change the model's behavior.
Access Control and Least Privilege
Limit access to AI models per user roles and responsibilities. Allow only approved personnel to enter prompts that affect critical operations, and apply the least privilege principle to diminish the possibility of misuse.
Output Monitoring and Anomaly Detection
Keep a constant watch on the outputs of AI systems for evidence of abnormal behavior (e.g., unexpected responses or actions that deviate from established protocols). Put in place mechanisms for anomaly detection that will identify and flag potential prompt injection attempts in real time.
Adversarial Testing and Red Teaming
Conduct adversarial testing and red teaming exercises regularly to imitate prompt injection attacks. This kind of proactive testing can help you to find vulnerabilities and ensure existing defenses are working, helping to improve an organization's security posture.
Human-in-the-Loop Oversight
Put systems for human oversight into place for important outputs generated by Artificial Intelligence. Include a human review process for responses, particularly in high-risk situations, to make sure that AI systems are acting ethically and with security in mind.
Regular Model Updates and Patches
Keep up to date with emerging changes in AI security and quickly install updates and patches for AI models. Routine maintenance guarantees models are secured against newly identified vulnerabilities and threats.
Vendor-Neutral Security Solutions
Implement artificial intelligence and enterprise-grade cybersecurity platforms that follow industry standards and best practices. Vendor-neutral solutions provide flexibility in how you address security and ensure that security is not reliant on iterative technology providers, resulting in maximizing system soundness.
Role of Cybersecurity Training and Certifications
As AI continues to find a place in enterprise systems, the need for adept professionals whose focus is on defending against AI-specific threats, such as prompt hacking, is increasing.
Cybersecurity Training programs focused on AI security can prepare skilled specialists to recognize and mitigate prompt injection attacks, keep sensitive information private, and promote safe AI use.
The USCSI® Institute offers complete and vendor neutral cybersecurity certifications focused on AI cybersecurity threats. The cybersecurity certifications provide training on prompt hacking mitigation, AI system monitoring, ethical considerations, and practical measures to secure large language models. It provides cybersecurity specialists with the knowledge to anticipate new AI threats and create robust and secure AI-enabled environments.
Conclusion
Prompt Hacking presents a new challenge, particularly with the rise of large language models (LLMs) in cybersecurity, which involves, instead of software vulnerabilities, the use of AI systems. Understanding minor prompt injection attacks, extracting lessons from real-life cases, and using strong barrier techniques can protect sensitive data and AI systems.
In the future, organizations should prioritize ransomware attacks, AI security, input validation, access controls, output monitoring, and human oversight, while also ensuring that they are investing in cybersecurity training from professionals and vendor-neutral certifications. Ultimately, expert human oversight will be part of navigating the evolving threat landscape for AI and will contribute to a safer and more secure digital future.