Machine Learning in Cybersecurity: Types, Use Cases, Challenges
A sudden burst of strange network traffic floods through corporate systems. It doesn’t match any known malware signature, nor are any security rules triggered. But within moments, sensitive corporate files are leaking out undetected. This isn’t a hypothetical situation—it’s the way modern cyberattacks happen today. Attackers no longer repeat the old patterns to perform cyberattacks; instead, they use advanced AI-assisted techniques, polymorphism, and many more.
As a result, to deal with advanced cyberattacks, overall information security spending will increase to approximately $240 billion in 2026, driven by the demand for AI-ML based security and threat detection capabilities (Gartner, 2025).
Unlike traditional tools, AI security tools and machine learning (ML) don’t just identify known threats — they predict abnormal activity, try to correlate to seemingly unrelated incidents, and adapt to constantly changing attack methods.
What is Machine Learning in Cybersecurity?
Machine learning (ML) in most areas is defined in academic literature as systems that learn patterns in data. If we talk about Machine Learning in cybersecurity, here’s how it works:
- Behavioral Modeling: ML identifies normal behavior across users, devices, processes, and networks. Instead of rigid rule-based measurement of deviations, it employs probabilistic deviation measurement.
- Adaptive Decision Making: ML goes beyond the traditional yes/no alert approach and provides dynamic threat scoring, risk triage, and automated response to threats.
- Failure Tolerant Learning: High-stakes environments are inevitable of attacks, and ML recognizes this highly smartly. Machine Learning flags areas of uncertainty to avoid cascading failures.
For instance, if a server that has never queried the internal databases does so all of a sudden, ML can mark it as high-risk. Now, let’s explore all types of ML in cybersecurity with their key machine learning applications for cybersecurity.
Stéphane Nappo, CISO and Thought Leader Qouted that “Cybersecurity isn’t just IT—it’s business resilience. Therefore, the need of advance security tools and technologies is increasing with every passing day.
Roles of Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
ML is transforming cybersecurity from a reactive process into an intelligent and proactive one. Want to know how? Here’s why:
- Real-time Telemetry: Process millions of events per second, with the ability to detect threats before a signature is available.
- Multi-Level Attack Reconstruction: Link low-level attack signals within hours, days, or weeks to rebuild attack patterns.
- False Positive Minimization: Prioritize alerts based on risk, so security professionals can concentrate on legitimate threats.
- Flexible Trust Scoring: Adjust risk scores for users, devices, and APIs to allow access based on trust that changes over time.
- Behavioral User & Entity Analytics(UEBA): Identify insider threats and misuse by learning behavior baselines.
- Operational Risk Prediction: Anticipate impact so you can respond to high-risk incidents first.
- Model Self-Monitoring: Avoid attacks on the ML models themselves, such as adversarial input or poisoning.
These abilities make machine learning in cybersecurity more and more crucial.
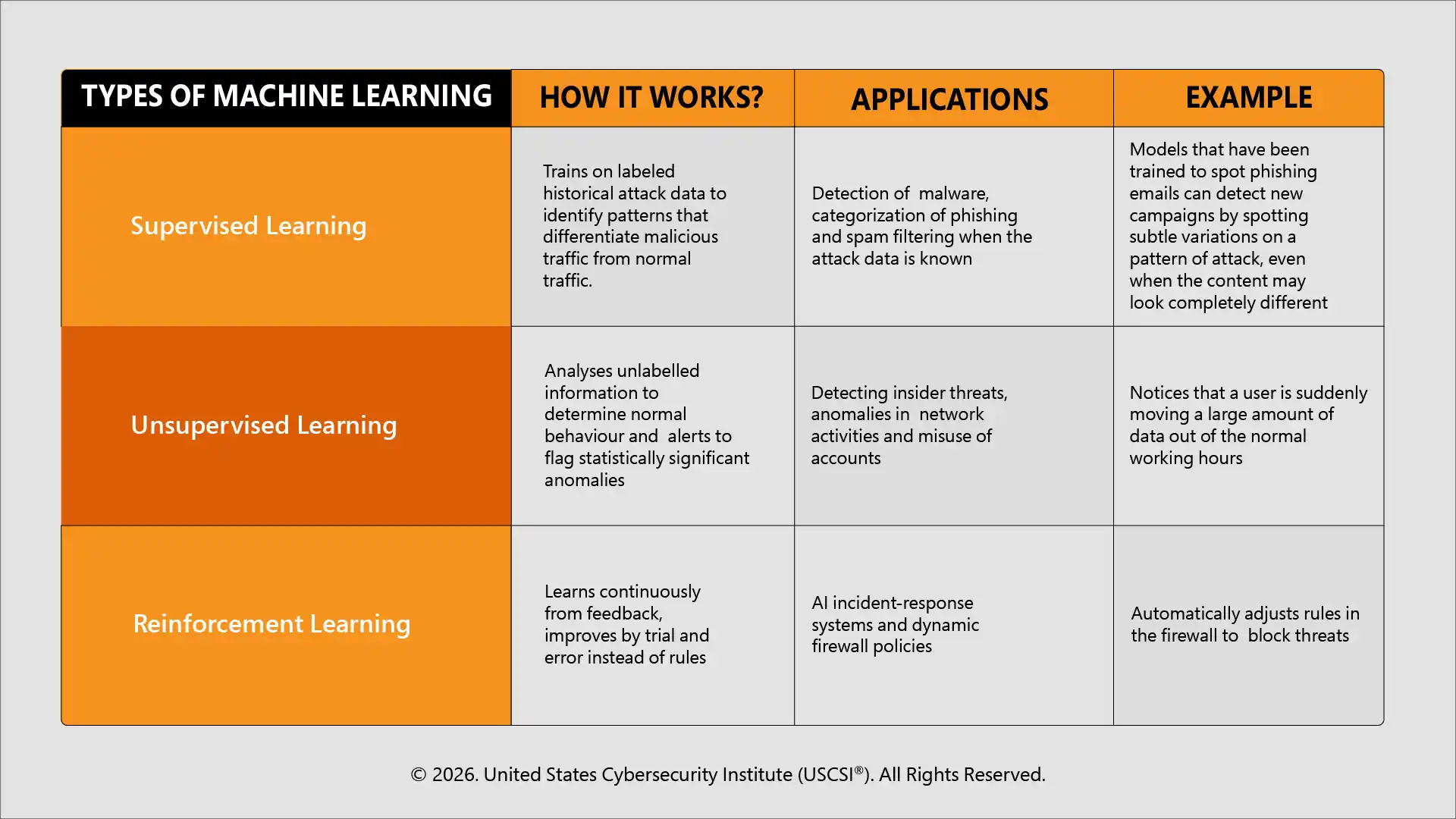
3 Types of Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
To understand AI and ML in cybersecurity, the table given below makes it easy to examine the operationally meaningful types of ML and their real-world examples in cybersecurity:
Major Use Cases of Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Let’s now explore the use cases of Machine Learning in Cybersecurity landscape in 2026. Here are the major use cases discussed below:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Identify never-seen-before attack vectors through historical tracking of network traffic, user activities, and access patterns.
- Malware Detection & Classification: Determine malware through behavior and context, not just static signatures, to protect against polymorphic threats.
- Phishing & Social Engineering Defense: Inspect URLs, emails, and sender methods to block attacks that get past common filters.
- Fraud Detection & Financial Security: Monitor transaction behavior in real time to identify abnormal fund transfer or account intrusion cases.
- Security Log Analysis & Event Correlation: Collect logs across everything in your environment to detect advanced, multi-stage attacks before harm is done.
- Attack Path Prediction: Anticipate how attackers may traverse networks, enabling preemptive blocking of attack paths.
- Security Debt Identification: Spotlight configurations and system settings that are statistically associated with future breaches for proactive resolution.
According to ZeroThreat.io, cybercriminals are reportedly freeing up to 60% of their time using AI-driven automation.
Read More: What are LLM Security Risks and Mitigation Plan for 2026
Challenges of Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
Did you know, as per Viking Cloud, more than 43 Percent of cyber criminals are more advanced than today’s internal cyber defense team? However, for all its benefits, ML in cybersecurity presents its own challenges:
- Adversarial Attack: Attackers craft input to evade ML detection, and thus need robust models.
- Data Quality & Labeling: It can all start with biased/inadequate training data that leads to a blind spot in the AI.
- Explainability & Trust: Analysts have to comprehend ML decision-making; black-box models can hamper adoption.
- Operational Complexity: Model orchestration, feature management, and continuous retraining are required.
- Wider Attack Surface: The ML pipelines can themselves be the target, so as to reduce detection or produce false positives.
To gain an in-depth understanding of today’s in-demand AI ML concepts and methodologies, explore top AI ML certifications such as USAII®’s Certified Artificial Intelligence Scientist (CAIS™) and Certified Artificial Intelligence Engineer (CAIE™), which can help you:
- Create durable and sustainable systems for ML security.
- Anticipate threats before they disrupt workflow.
- Develop leading ML models for cyber defence.
Upskill to keep pace with the evolving and advancing technologies applied in today’s cybersecurity landscape.
Final Takeaways
Building and deploying ML-powered cybersecurity systems demands in-depth expertise. Not just programming, or foundational cybersecurity and ML knowledge will be enough today to deal with advanced cyber threats; professionals need to know model risk, adversarial attacks, and operational deployment.
Cyberattacks have become more complex, as they advance in ways that are almost impossible to predict. These attacks are designed to exploit vulnerabilities that go unnoticed and can easily outpace any “rules-based” defense systems. Upskill with today’s most wanted cybersecurity skills, such as AI-driven threat detection, to become a cybersecurity specialist who stays ahead of modern cyberattacks.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How do organizations defend ML systems from poisoning attacks?
Through robust model validation, continuous monitoring, and anomaly detection in training pipelines.
2. Can ML models quantify operational and financial risk, not just technical risk?
Yes—advanced ML systems integrate behavior analysis with business impact scoring.
3. How can security teams validate ML performance without exposing models to attackers?
By using secure test environments, synthetic data, and sandbox simulations.
4. What governance and audit mechanisms are essential for AI-driven security systems?
Version control, retraining logs, access auditing, and model explainability protocols are critical.