Data Security Explained: Why It’s Vital in the Digital Era
Data security refers to the act of safeguarding digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, and theft, while ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the data. Technologies and methods such as encryption, biometric verification, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) are utilized to maintain the security of the data while it is both in transit and at rest.
According to the Accenture State of Cybersecurity Resilience 2025 report, 77% of organizations lack even the most foundational security practices around data and AI, leaving their systems, models, and cloud infrastructure exposed to modern data security threats.
These security gaps are not just vulnerabilities; they are systemic blind spots that need to be addressed to build resilient and secure digital environments. Let’s dive into why data security matters and how organizations may be able to better defend themselves.
Why Data Security Matters in the Age of Digital Transformation
The accelerated speed of digital transformation, which involves the convergence of cloud platforms, mobile computing, AI, and IoT, is significantly expanding the attack surface and, in turn, making data protection paramount. Organizations risk falling prey to ransomware attacks, data breaches, and the loss of customer trust if they don't take proper safeguards.
Data security safeguards not only protect business-critical data but also help organizations:
- Achieve compliance with data privacy regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
- Protect brand reputation and ensure privacy, which builds trust.
- Support operational continuity with a resilient recovery structure.
Real-World Impact of Poor Data Security
- Qilin Ransomware Attack on Asahi Group:
Hackers attacked Japan's Asahi Group and shut down six production sites. They also stole more than 9,300 files (27 GB) of sensitive material. That incident shows how ransomware can stop production and hurt a company’s reputation.
- Kido Nurseries Data Breach:
A cyberattack made the personal information of policy of approximately 8,000 children in London publicly available. The attackers leaked the personal profiles of 10 children and threatened to leak more profiles unless payment was made. The breach highlights how weak security affects privacy and trust.
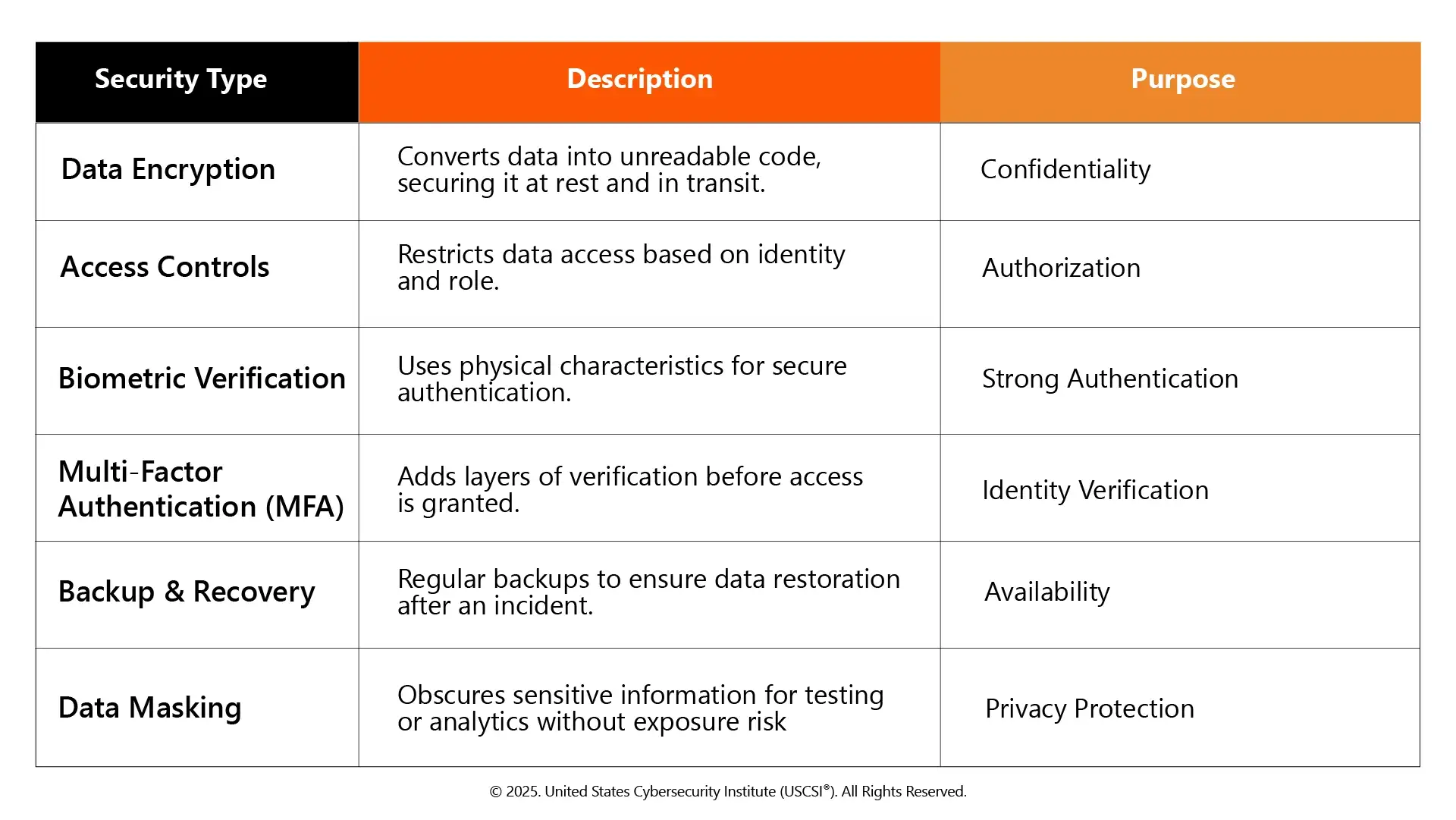
Types of Data Security Measures & InfoSec Strategies
The goal of information security (InfoSec) strategies is to safeguard data in on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments. The most typical data security types consist of:
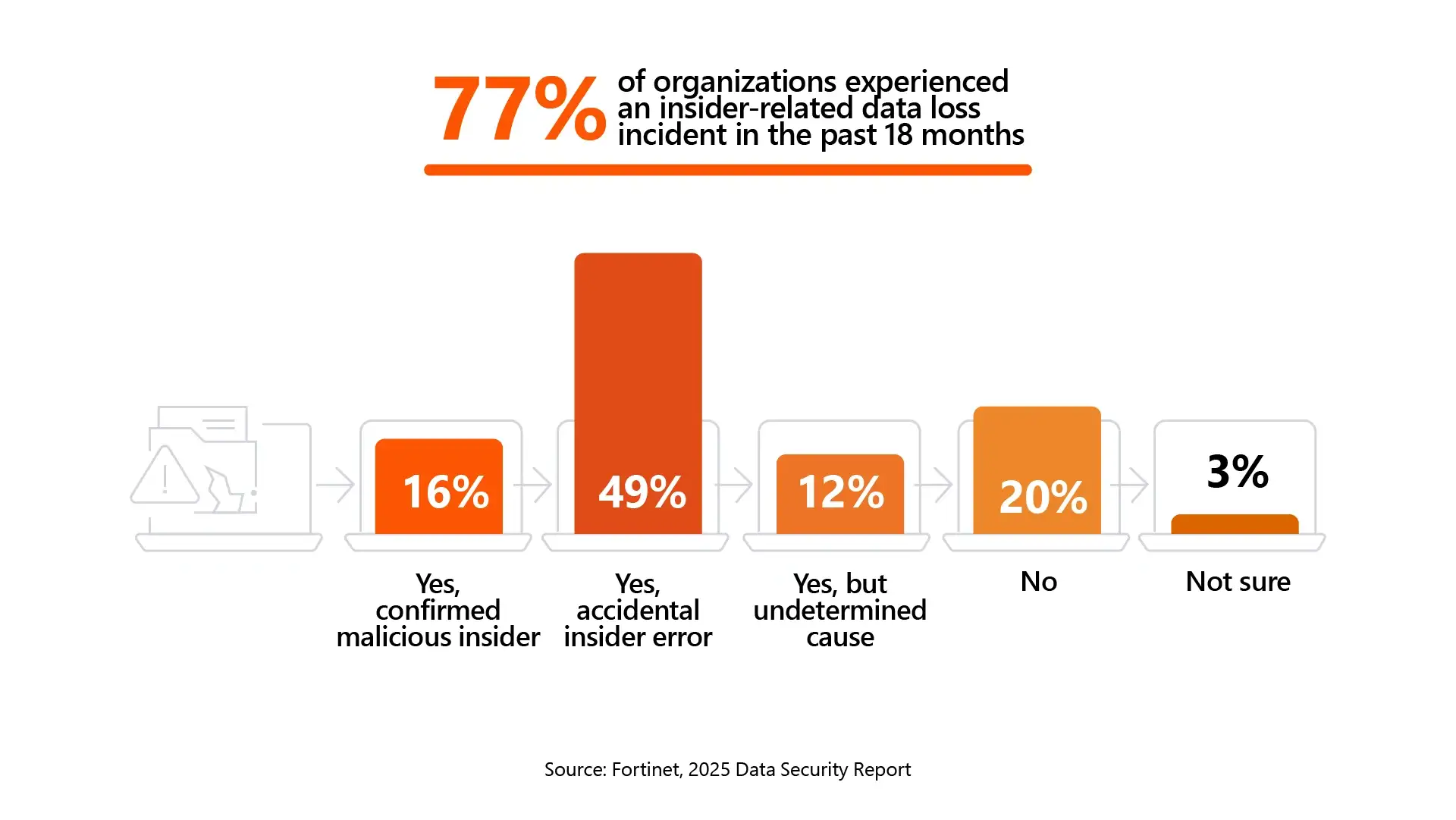
Data Security Risks and Threats
There are many evolving potential threats to an organization’s data. Acknowledging the risks and threats to an organization’s data security risk and threats is the first step in putting in place solid protections against them.
The most prevalent threat is insider threat, which involves a person with authorized access, such as a partner, contractor, or employee, who purposefully or unintentionally misuses their access to data to compromise the data, systems, or operations of the company.
Some other common threats are:
- Ransomware Attacks: This is malware that encrypts files and demands a ransom to decrypt them. This is one of the fastest-evolving, most damaging, and costliest threats today.
- Data Breaches: This is unauthorized access to sensitive data. These are sometimes the result of poor controls.
- Phishing, Social Engineering: Trick employee(s) into revealing credentials.
- System Misconfigurations: Improper security settings, leaving the system exposed.
- Human Error: Inadvertently exposing data due to a lack of security awareness.
- Natural Disasters: Such as power outages or physically damaging data systems.
It is important to have modern cybersecurity tools that utilize AI-driven detection, intrusion prevention systems, or 24-hour monitoring to mitigate the risks described above.
Data Security Regulations and Compliance Requirements
Regulatory compliance is part of a comprehensive InfoSec plan. Organizations have to comply with worldwide standards to protect themselves and establish trust with the customer:
- GDPR: Requires organizations to protect the Personal Data of EU citizens and to ensure transparency in processing data
- CCPA: Gives California residents the right to request access to and deletion of their Personal Data.
- HIPAA: Requires that you implement security controls for sensitive health data.
- PCI DSS: Protects cardholder data through encryption and access controls.
Non-compliance can be costly, including fines and damage to reputation. Compliance is no longer a legal obligation but rather a competitive advantage.
Understanding the Relationship Between Data Security and Data Privacy
Although the terms "data security" and "data privacy" are used interchangeably, they refer to different but interrelated aspects of protecting data.
- Data security is concerned with protecting data from a breach using mechanisms such as encryption, access controls, or even biometric authentication to ensure sensitive information is secure.
- On the other hand, data privacy is concerned with how data is collected, used, and shared to ensure compliance with regulations and to respect the consent of the user.
Together, both data security and data privacy serve as two pillars to a strong cybersecurity framework, not only to ensure data is secure but also to make sure it is used responsibly.
Emerging Data Security Trends in 2026
The future of data security is influenced by the emergence of different technologies and changing threat vectors. In 2026, key trends in cybersecurity will include:
-
AI and Automation in Cybersecurity: AI capabilities are enhancing technology in multiple ways, including improving threat detection, predicting threat behavior, and automating responses to threats, allowing for improved efficiencies and a proactive stance when it comes to data security.
-
Multicloud Security: As organizations embrace digital transformation, consistent protection across cloud providers is becoming a necessity for businesses.
-
Post-Quantum Cryptography: The industry will work to develop encryption that protects against quantum threats. Quantum computing introduces a new range of threats to traditional methods of encryption, which businesses need to be prepared for.
-
Security Mesh Architecture: Organizations are moving security from the perimeter to the data layer because of the dynamic nature of the cloud.
-
Zero Trust Security: Zero trust security requires businesses to verify identity and access continuously to protect against internal threats while also guarding against external threats.
Also, know more about the Top 8 Cybersecurity Trends to Watch Out in 2026
Best Practices for Effective Data Security
To remain vigilant to potential threats and support digital transformation, organizations should adopt the following principles:
- Classify and encrypt sensitive data.
- Use biometric verification and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- Implement least privilege access.
- Utilize cybersecurity tools that can perform real-time monitoring and threat detection.
- Train employees through cybersecurity training programs.
- Practice regular audits and penetration testing.
- Maintain strong backup and disaster recovery protocols.
- Align with regulatory compliance frameworks.
Conclusion
As digital transformation continues, protecting sensitive data is more important than ever. Strong data security, supported by strategies like encryption, biometric verification, and multi-factor authentication, helps organizations stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain trust.
For those looking to grow in the field, staying updated on cybersecurity trends and building skills is essential. Enrolling in a cybersecurity training programs with the United States Cybersecurity Institute (USCSI®) can be a valuable step toward strengthening expertise and confidently navigating the future of cybersecurity.